

- Core Center:National Institute for Basic Biology
- Principal Investigator:Kiyoshi Naruse
- FAX:+81-564-55-7580
- Sub-Core Center 1:Center for Bioscience Research and Education, Utsunomiya University
- Sub-Core Center 2:Department of Genomics and Evolutionary Biology, National Institute of Genetics
- Sub-Core Center 3 (Backup):Faculty of Regional Innovation, University of Miyazaki
概要Overview
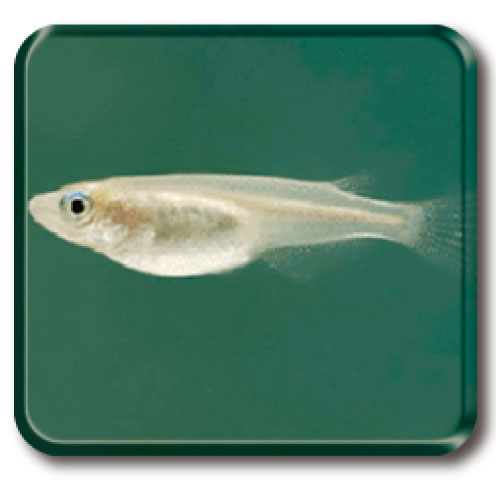
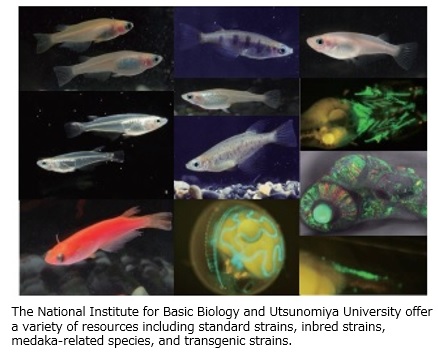 Medaka is a small freshwater fish with a relatively short life cycle (3 months) and small genome size (800 Mbp). Medaka can adapt to low temperatures (4℃) in the winter and high temperatures (40℃) in the summer, as well as to relatively high salinity environments. In addition to medaka, the NBRP also provides medaka-related species and hatching enzymes essential for embryonic manipulation, along with high quality genome sequence information and genome annotations.
Medaka is a small freshwater fish with a relatively short life cycle (3 months) and small genome size (800 Mbp). Medaka can adapt to low temperatures (4℃) in the winter and high temperatures (40℃) in the summer, as well as to relatively high salinity environments. In addition to medaka, the NBRP also provides medaka-related species and hatching enzymes essential for embryonic manipulation, along with high quality genome sequence information and genome annotations.
Stock
・Standard strains and wild-derived strains from Japan,China, and Korea: about 100 strains
・Mutant and transgenic lines: about 730 strains
・Related species: about 10 strains
・Genome resources (cDNA, BAC, Fosmid clones): about 730,000 clones
・Hatching enzymes
Subjects in the NBRP programs “Genome information upgrading program” and “Fundamental technology upgrading program” related to “Medaka”
【 Genome information upgrading program 】
| FY2010 | Micro-Tom BAC end sequencing |
| FY2009 | Full-length cDNA resources of Medaka fish |
| FY2008 | Full-length cDNA resources of Medaka fish |
| FY2007 | Full-length cDNA resources of Medaka fish |
| FY2002 | Genome Information Upgrading Program : FY2002-FY2006 |
